Options trading, often considered a realm for the financially astute, can be a lucrative venture when approached with the right knowledge and strategy. In this blog post, we’ll unravel the fundamentals of options trading, breaking down the jargon and complexities to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of how options work and how you can start your journey in this exciting financial domain.
Options trading, simply put, provides the opportunity to buy or sell a particular financial instrument at a specified price, known as the “strike price,” within a predetermined timeframe. The allure of options lies in their flexibility, enabling investors to capitalize on market movements, hedge against risks, and optimize their portfolio performance.
In this exploration of options trading basics, we’ll cover what options are, the types of options available, how they function, and key terminologies associated with this dynamic market. By the end, you’ll have a solid foundation to venture further into the world of options trading.
II. What Are Options?
Options, in the world of finance, are contracts that grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price before or at the contract’s expiration date. This predetermined price is known as the “strike price.” The buyer of the option pays a premium for this right.
Types of Options:
1. Call Options:
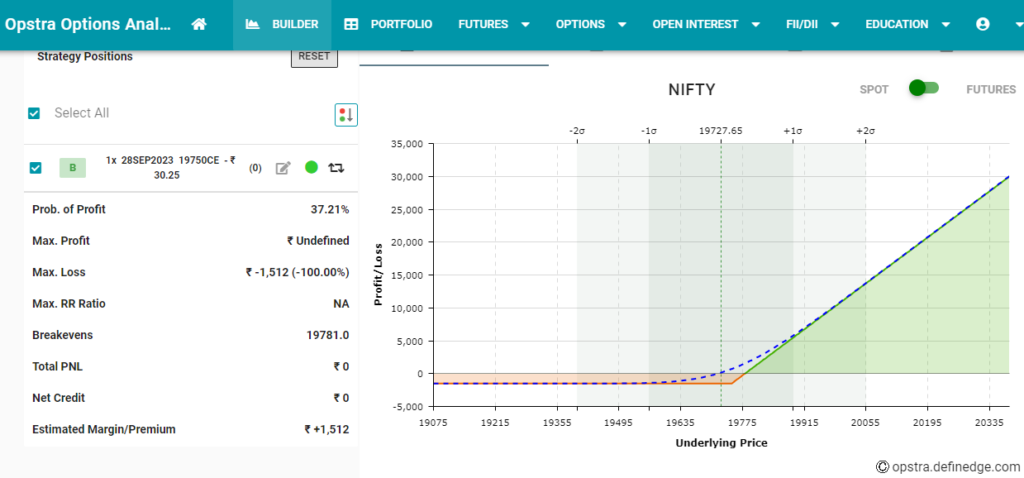
- Definition: A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price before the option’s expiry.
- Purpose: Traders buy call options when they anticipate the price of the underlying asset will rise, allowing them to profit from the price difference.
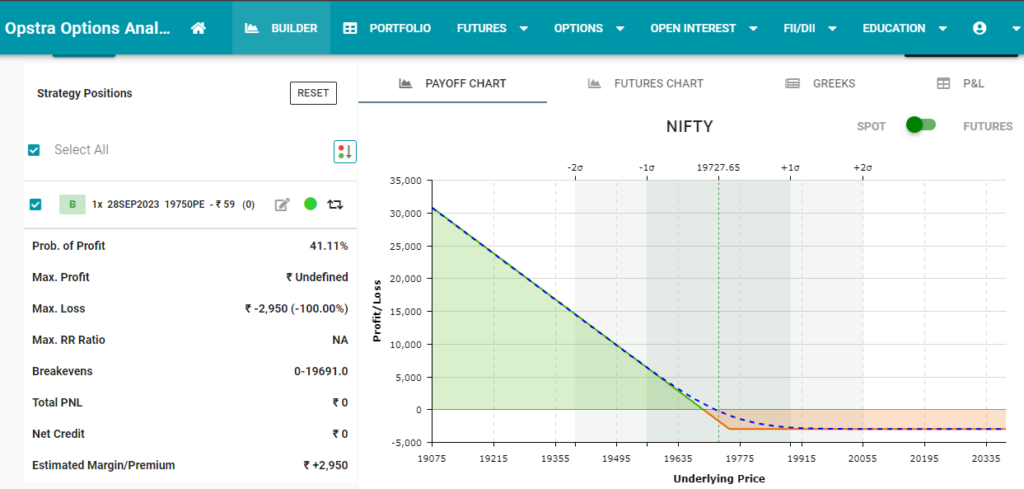
2. Put Options:
- Definition: A put option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price before the option’s expiry.
- Purpose: Traders buy put options when they predict the price of the underlying asset will fall, enabling them to profit from the price decline.
III. Types of Options Based on Exercising
1. American Options:
- Holders can exercise the option any time before the option’s expiration date.
- Offers more flexibility for strategic decisions.
2. European Options:
- Holders can only exercise the option at the expiration date.
- Offers less flexibility compared to American options.
Understanding these fundamental types of options is pivotal in comprehending how options operate and the different strategies that can be implemented when trading them.
III. Understanding How Options Work
1. Option Premium:
- The price paid by the option buyer to the seller for the rights provided by the option contract.
- Factors influencing the premium include the strike price, time to expiration, and market conditions.
2. Expiration Date:
- The date on which the option contract expires and becomes invalid.
- After the expiration date, the option loses its value and ceases to exist.
3. Strike Price (Exercise Price):
- The predetermined price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying asset.
- Determines the break-even point and potential profitability of the option.
4. In-the-Money (ITM):
- A situation where exercising the option would result in a profitable position.
- For call options: When the market price is higher than the strike price.
- For put options: When the market price is lower than the strike price.
5. Out-of-the-Money (OTM):
- A situation where exercising the option would not be profitable.
- For call options: When the market price is lower than the strike price.
- For put options: When the market price is higher than the strike price.
IV. Key Options Trading Strategies
Options trading opens up a plethora of strategic possibilities. Some popular strategies include:
- Covered Call
- Long Straddle
- Bull Call Spread
- Bear Put Spread
Understanding these strategies can help you make informed decisions when trading options.
IV. Key Options Trading Strategies
Options trading provides a spectrum of strategies, each designed to suit varying market conditions and trader objectives. Here are some fundamental strategies to kickstart your options trading journey:
1. Covered Call:
- Strategy: Involves holding a long position in an asset while simultaneously writing (selling) call options on the same asset.
- Objective: Generate income through premium collection from selling the call options.
2. Long Straddle:
- Strategy: Involves buying a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
- Objective: Benefit from significant price movements of the underlying asset, regardless of the direction.
3. Bull Call Spread:
- Strategy: Involves buying a call option and simultaneously selling another call option with a higher strike price but the same expiration date.
- Objective: Profit from a moderately bullish market outlook with limited risk.
4. Bear Put Spread:
- Strategy: Involves buying a put option and simultaneously selling another put option with a lower strike price but the same expiration date.
- Objective: Profit from a moderately bearish market outlook with limited risk.
Understanding these strategies is essential for developing a versatile approach to options trading. Each strategy has its risk-reward profile and is suited for different market conditions.
Options trading, though initially daunting, offers an array of strategies and possibilities for traders and investors. From the foundational concepts to the diverse range of strategies, this blog post has provided a glimpse into the exciting world of options.
Armed with knowledge about call and put options, key terminologies, and fundamental strategies, you’re well-equipped to take your first steps into options trading. Remember, practice and continuous learning are key to mastering the art of options trading.
As you embark on your options trading journey, always prioritize thorough research, risk management, and a strategic approach. The world of options is dynamic, and successful trading demands adaptability and discipline.
May this newfound understanding of options trading pave the way for profitable ventures and strategic financial growth.
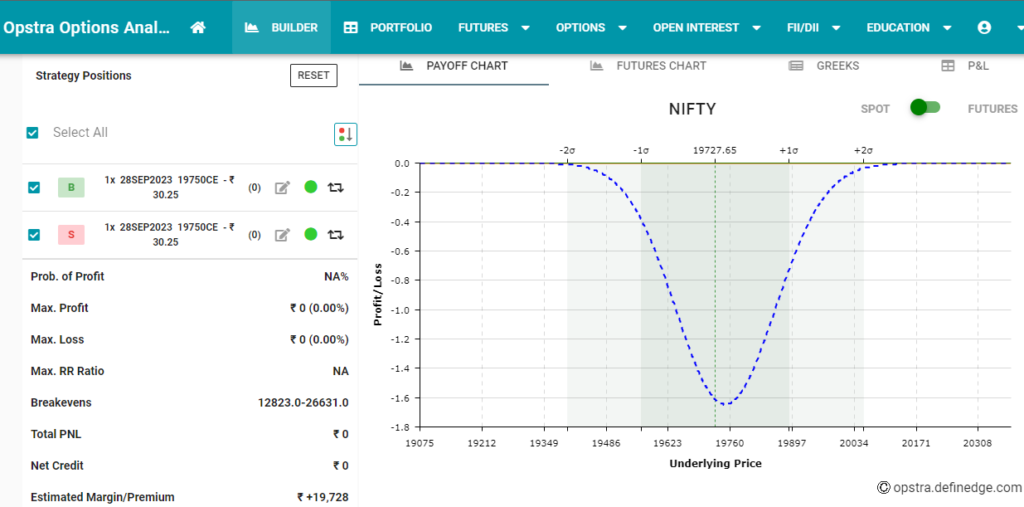
Covered Call Strategy: Enhancing Portfolio with Option Premiums
Options trading offers a plethora of strategies, each designed to suit different risk appetites and financial goals. For those stepping into the world of options, the Covered Call strategy stands as an appealing starting point. It not only allows you to potentially enhance your portfolio but also provides a way to generate regular income through option premiums.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the Covered Call strategy, dissecting its mechanisms, understanding the risks and rewards, and discovering how you can strategically employ it to optimize your investment portfolio. Whether you’re a newcomer to options trading or a seasoned investor looking to refine your strategies, understanding the Covered Call strategy is a crucial step towards financial growth and stability.
Let’s embark on this enlightening journey, unwrapping the core concepts and strategies that define the Covered Call approach
II. Understanding the Covered Call Strategy
The Covered Call strategy is a popular and relatively conservative options trading approach. It involves two main components: owning shares of a particular stock and simultaneously selling call options against those shares. The call options are sold at a strike price and an expiration date predetermined by the seller.
In this strategy:
- You own the underlying stock: This provides security and aligns your interests with the strategy.
- You sell call options (contracts to buy the stock) to another investor: You earn a premium for selling these options, which adds to your income.
The goal is to benefit from the premiums received by selling call options while still holding onto the stock for potential capital appreciation.
Objectives of the Covered Call Strategy:
- Income Generation: Earn premiums from selling call options.
- Portfolio Enhancement: Potentially enhance the overall return of your stock investments.
- Risk Management: Reduce the effective purchase cost of the underlying stock.
Understanding the dynamics of this strategy is crucial to utilizing it effectively in your investment endeavors. In the upcoming sections, we’ll delve into how to implement the Covered Call strategy, the risks involved, and tips for maximizing its benefits.
III. Implementing the Covered Call Strategy Effectively
Implementing the Covered Call strategy involves a strategic approach to both owning the underlying stock and selling call options. Here’s a step-by-step guide to effectively execute this strategy:
Step 1: Choose the Underlying Stock
- Opt for a stock you’re willing to hold for the long term.
- Consider stocks with moderate volatility and a steady price history.
Step 2: Assess the Call Options
- Select call options that expire after a reasonable period, typically 30 to 60 days.
- Evaluate the strike price based on your expectations for the stock’s price movement.
Step 3: Sell Call Options
- Determine the number of call options to sell based on the number of shares you own.
- Sell the call options, earning a premium.
Step 4: Monitor and Manage
- Regularly monitor the stock’s performance and market conditions.
- Be prepared to buy back the options if needed, or let them expire if the stock price remains below the strike price.
By following these steps and maintaining a disciplined approach, you can effectively utilize the Covered Call strategy to enhance your portfolio and generate consistent income.
In the subsequent sections, we’ll delve into the risks associated with this strategy, provide tips for success, and summarize the key takeaways from employing the Covered Call approach.
IV. Risks of the Covered Call Strategy
While the Covered Call strategy is relatively conservative, it’s essential to be aware of the risks involved to make informed decisions. Here are the primary risks associated with this strategy:
1. Limited Upside Potential:
- By selling call options, you may cap your potential gains if the stock’s price surges significantly beyond the strike price.
2. Stock Depreciation Risk:
- If the stock price significantly decreases, the premium received may not sufficiently offset the paper loss from owning the stock.
3. Opportunity Cost:
- If the stock price rises dramatically, you may miss out on potential higher profits by selling the stock at the strike price.
4. Obligation to Sell:
- Selling call options obliges you to sell the stock at the strike price, even if you believe the stock’s value will increase further.
Understanding these risks allows you to employ risk management strategies and make informed choices when implementing the Covered Call strategy.
V. Tips for Success with the Covered Call Strategy
To effectively utilize the Covered Call strategy and optimize your investment portfolio, consider the following tips:
1. Choose the Right Stocks:
- Opt for stocks of companies you believe in and are willing to hold for the long term.
2. Strike Price Selection:
- Choose a strike price that aligns with your expectations for the stock’s price movement.
3. Market Research and Analysis:
- Conduct thorough research and stay updated with market trends to make informed decisions.
4. Practice Risk Management:
- Set stop-loss orders to mitigate potential losses and protect your investment.
5. Regularly Monitor and Adjust:
- Stay vigilant, monitor the stock’s performance, and be prepared to adjust your strategy as needed.
By incorporating these tips into your strategy, you can enhance your success rate and effectively navigate the dynamics of options trading.
In utilizing the Covered Call strategy, here are the essential takeaways to remember:
- Income Generation: The strategy offers a regular stream of income through option premiums, enhancing your overall returns.
- Risk Mitigation: While reducing the cost basis of owning the stock, the strategy provides a cushion against potential losses.
- Strategic Approach: Implement the strategy by carefully selecting the underlying stock, strike prices, and expiration dates.
By embracing these takeaways and implementing the Covered Call strategy strategically, you can optimize your investment portfolio and work towards financial growth.
The Covered Call strategy is a versatile and relatively conservative approach to options trading. It allows you to not only enhance your portfolio but also generate regular income through option premiums. By understanding the risks, following best practices, and implementing this strategy strategically, you can optimize your investment endeavors.
As you embark on your options trading journey, always remember to align the strategy with your financial goals and risk tolerance. With dedication, continuous learning, and a thoughtful approach, the Covered Call strategy can become a valuable tool in your investment toolkit.
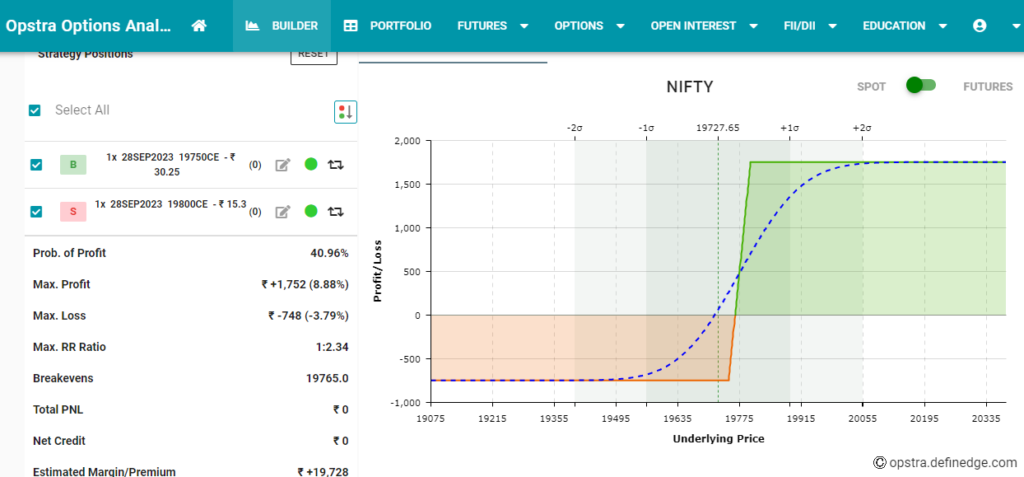
Long Straddle Strategy: Profiting from Market Volatility
Options trading provides an array of strategies for investors to profit from market movements. One such strategy, the Long Straddle, stands out for its potential to capitalize on volatility in the financial markets. The Long Straddle is a versatile options strategy that allows traders to benefit from significant price swings, regardless of the direction.
In this comprehensive guide, we will demystify the Long Straddle strategy, exploring its mechanics, understanding when to employ it, and highlighting its benefits and risks. Whether you’re new to options trading or seeking to broaden your strategic repertoire, understanding the Long Straddle strategy can enhance your ability to navigate the market’s ups and downs.
Let’s embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the intricacies of the Long Straddle strategy.
V. Tips for Success with the Long Straddle Strategy
Maximize the potential of the Long Straddle strategy with these actionable tips:
- Choose the Right Underlying Asset: Opt for highly volatile assets to increase the likelihood of substantial price movements.
- Time Your Trades Wisely: Execute the strategy closer to anticipated events or expected volatility spikes for maximum impact.
- Manage Risk Effectively: Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and secure profits if the trade moves favorably.
- Stay Informed: Keep track of market events, earnings announcements, or economic indicators that could impact the asset’s price.
VI. Enhancing Your Toolkit: Bull Call Spread
Introduction to Bull Call Spread:
- The Bull Call Spread is an options trading strategy used when an investor expects a moderate increase in the price of the underlying asset.
- It involves buying a lower-strike call and simultaneously selling a higher-strike call of the same expiration date.
- This strategy offers limited risk and limited profit potential.
Mechanics of a Bull Call Spread:
- The strategy involves two call options: buying a lower-strike call (long call) and selling a higher-strike call (short call).
- The long call benefits from price increases, while the short call helps mitigate the cost of the long call.
- The goal is to profit from a moderate price increase in the underlying asset.
Key Advantages:
- Limited Risk: The overall cost of the trade is reduced by selling the higher-strike call, limiting potential losses.
- Lower Break-Even Point: The strategy allows for a wider range of profitability compared to simply buying a call option.
- Profit Potential: If the asset’s price increases moderately, this strategy can yield a solid profit.
Scenarios Ideal for Employing a Bull Call Spread:
- Moderate Bullish Outlook: When you anticipate a moderate rise in the asset’s price but want to reduce the cost of entering a bullish position.
- Limited Investment Capital: If you have limited funds and seek a strategy with defined risk and lower upfront costs.
By understanding the ideal scenarios for employing a Bull Call Spread, you can effectively incorporate this strategy into your trading toolkit.
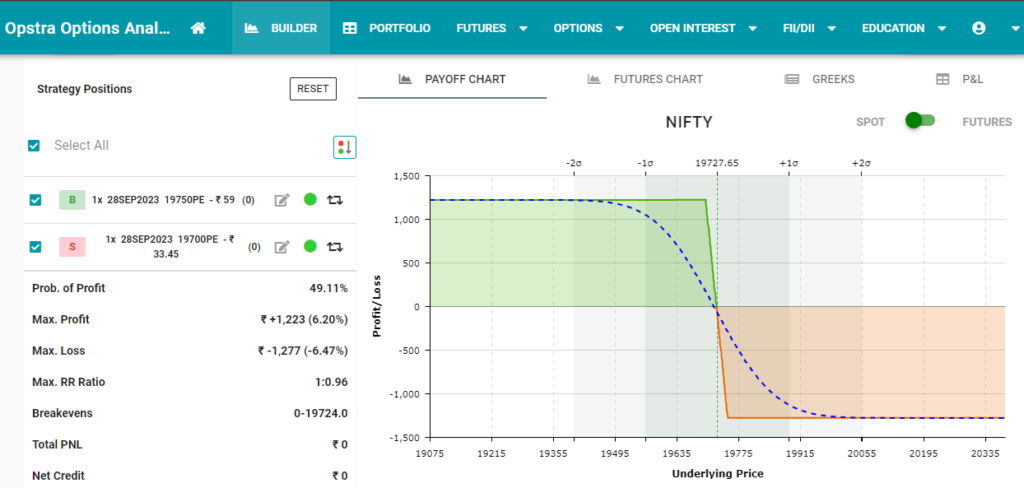
VII. Expanding Your Horizons: Bear Call Spread
Introduction to Bear Call Spread:
- The Bear Call Spread is an options strategy suitable when you expect a moderate decrease in the price of the underlying asset.
- It involves selling a lower-strike call and simultaneously buying a higher-strike call of the same expiration date.
- This strategy offers limited profit potential and defined risk.
Mechanics of a Bear Call Spread:
- The Bear Call Spread strategy involves two call options: selling a lower-strike call (short call) and buying a higher-strike call (long call).
- The short call aims to profit from a decrease in the underlying asset’s price, while the long call limits potential losses.
- The goal is to generate income while maintaining limited risk in a bearish market.
Key Advantages:
- Limited Risk: The risk is defined and limited to the difference in strike prices minus the premium received.
- Income Generation: By selling a call, you receive a premium, providing immediate income.
- Bearish Positioning: Profits are made if the asset’s price remains below the sold call’s strike price.
Scenarios Ideal for Employing a Bear Call Spread:
- Moderate Bearish Outlook: When you anticipate a moderate decline in the asset’s price and want to generate income with limited risk.
- Neutral to Slightly Bearish Sentiment: If you expect the asset’s price to remain relatively stable or decline slightly.
Understanding the opportune scenarios for utilizing a Bear Call Spread allows for strategic integration of this approach into your options trading.
VIII. Key Takeaways: Mastering Options Strategies
1. Long Straddle Strategy:
- Ideal for anticipating significant price movement.
- Involves buying a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
- Aims to profit from volatility, offering unlimited potential gains.
2. Bull Call Spread:
- Effective for a moderate bullish outlook.
- Involves buying a lower-strike call and selling a higher-strike call.
- Offers limited risk and lower break-even points compared to a simple call purchase.
3. Bear Call Spread:
- Suitable for a moderate bearish outlook.
- Involves selling a lower-strike call and buying a higher-strike call.
- Provides limited risk and the opportunity to generate income.
The Long Straddle, Bull Call Spread, and Bear Call Spread are valuable strategies in an options trader’s toolkit. Understanding their mechanics, risks, and optimal scenarios for use empowers traders to navigate varying market conditions effectively.
Integrate these strategies thoughtfully, considering your market outlook and risk tolerance. Continuous learning and practical application will sharpen your options trading skills, enhancing your ability to achieve financial goals.
Happy trading!


